@
- 前言
- 一、OpenCV DNN模块
- 二、TensorFlow pb文件的生成和调用
- 1.TensorFlow2 Keras模型(mnist)
- 2.使用Keras搭建cnn训练mnist(train.py),训练部分源码如下:
- 3.训练结果保存成冻结模型(pb文件)(train.py),训练结果保存为冻结模型的源码如下:
- python-opencv调用冻结模型cvcallpbpy" rel="external nofollow noreferrer">4.python opencv调用冻结模型(cvcallpb.py)
- 三、LabVIEW OpenCV DNN实现手写数字识别
- 四、源码下载
- 总结
前言
今天和大家一起来看一下在LabVIEW中如何使用OpenCV DNN模块实现手写数字识别
一、OpenCV DNN模块
1.OpenCV DNN简介
OpenCV中的DNN(Deep Neural Network module)模块是专门用来实现深度神经网络相关功能的模块。OpenCV自己并不能训练神经网络模型,但是它可以载入别的深度学习框架(例如TensorFlow、pytorch、Caffe等等)训练好的模型,然后使用该模型做inference(预测)。而且OpenCV在载入模型时会使用自己的DNN模块对模型重写,使得模型的运行效率更高。所以如果你想在OpenCV项目中融入深度学习模型,可以先用自己熟悉的深度学习框架训练好,然后使用OpenCV的DNN模块载入。
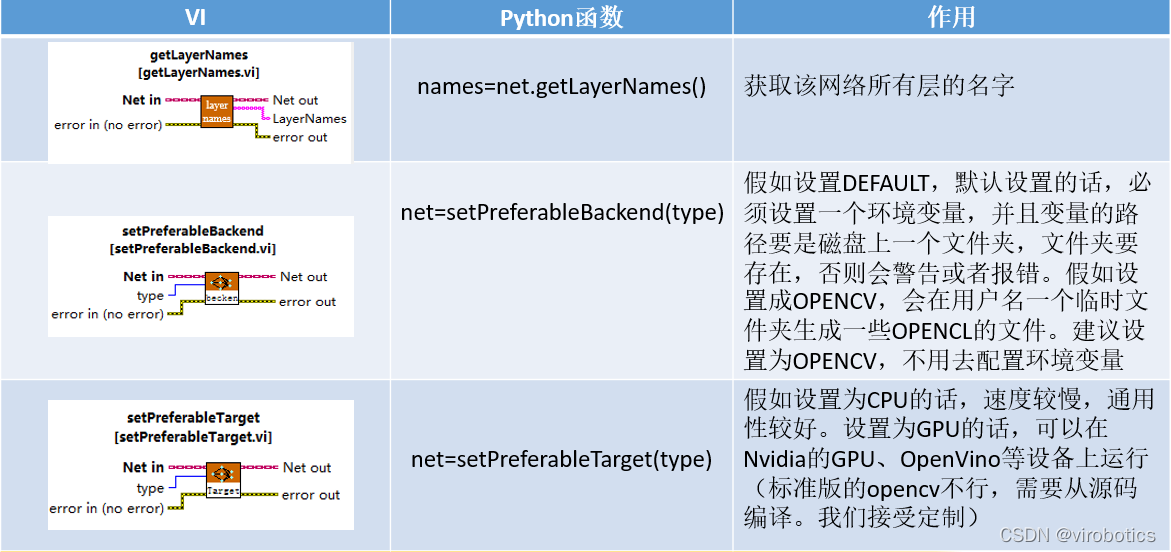
2.LabVIEW中DNN模块函数
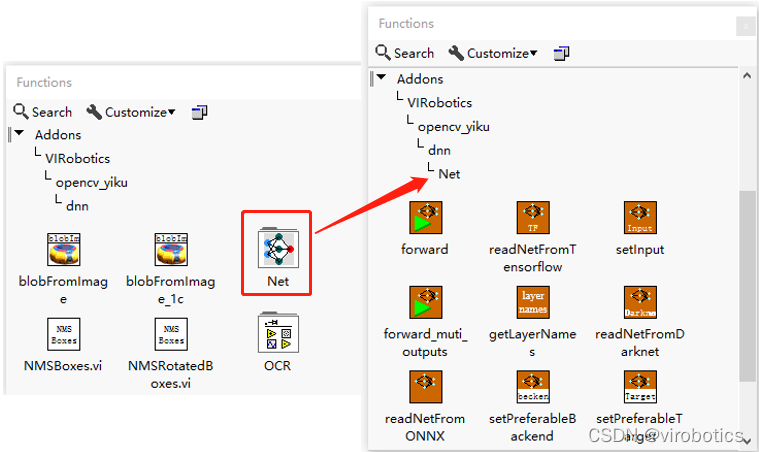
DNN模块位于程序框图-函数选板-Addons-VIRobotics-opencv_yiku中,如下图所示:
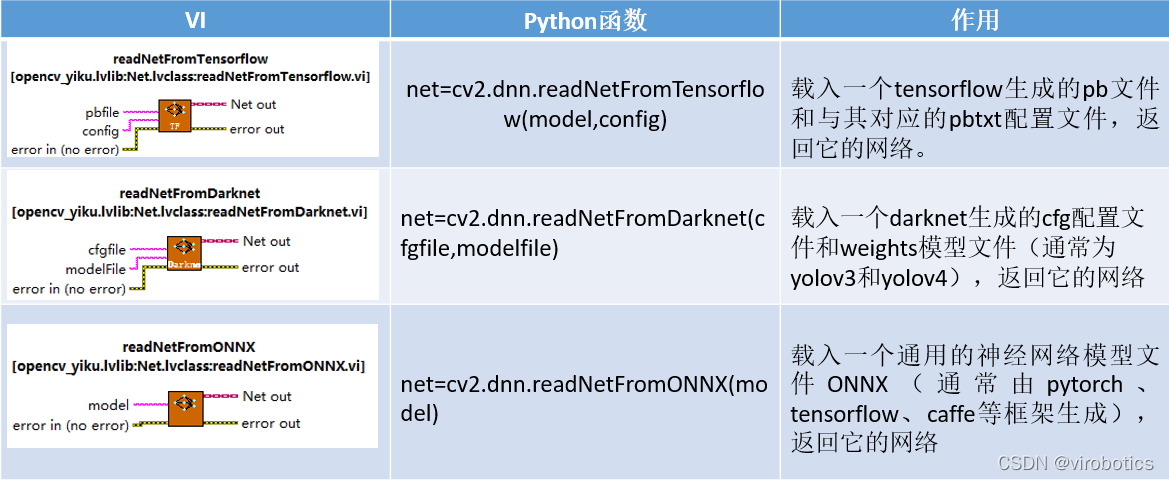
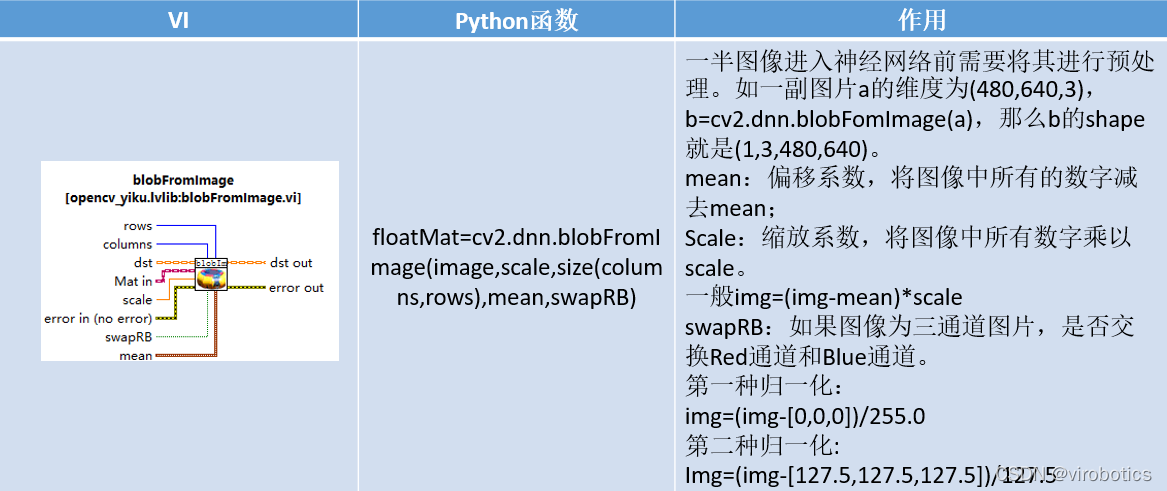
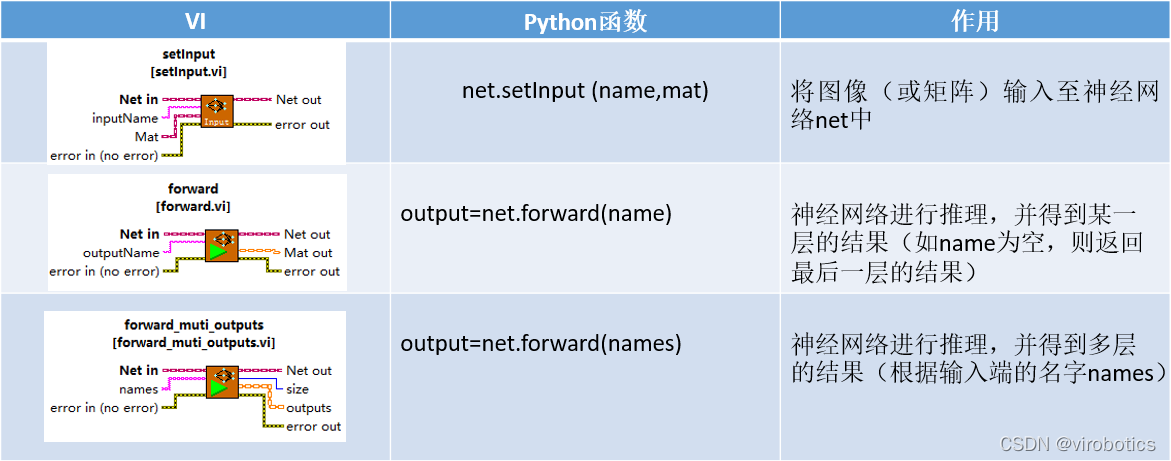
 Net选版中的函数与python中的函数对比如下:
Net选版中的函数与python中的函数对比如下:
二、TensorFlow pb文件的生成和调用
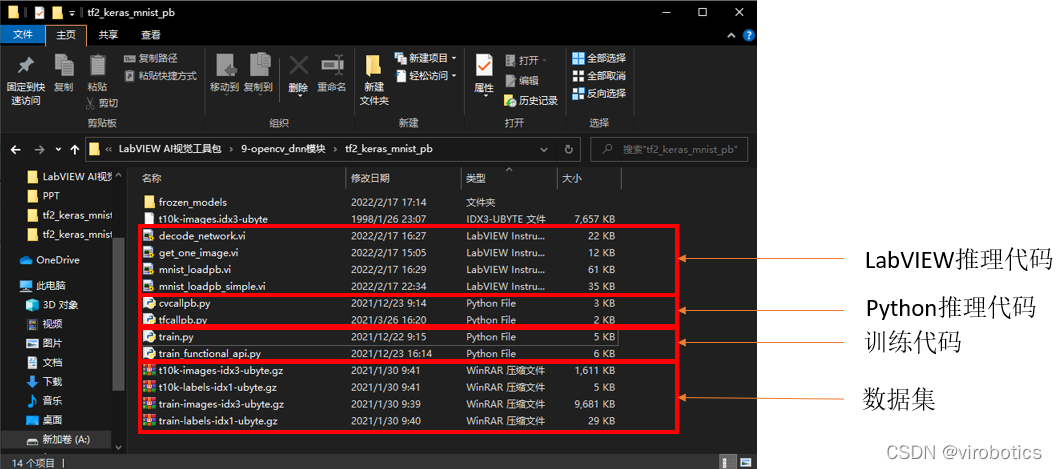
1.TensorFlow2 Keras模型(mnist)
注:本范例必须使用tensorflow 2.x版本
如下图所示所示为数据集以及LabVIEW与Python推理和训练代码,相关源码可在链接中下载。
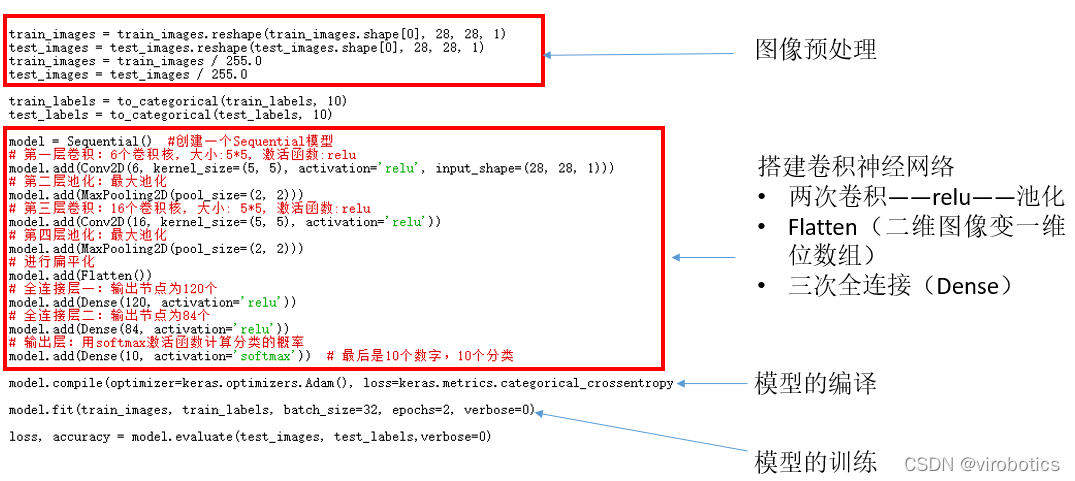
2.使用Keras搭建cnn训练mnist(train.py),训练部分源码如下:
train_images = train_images.reshape(train_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1)
test_images = test_images.reshape(test_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1)
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels, 10)
test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels, 10)
model = Sequential() #创建一个Sequential模型
# 第一层卷积:6个卷积核, 大小:5*5, 激活函数:relu
model.add(Conv2D(6, kernel_size=(5, 5), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
# 第二层池化:最大池化
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
# 第三层卷积:16个卷积核, 大小: 5*5, 激活函数:relu
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=(5, 5), activation='relu'))
# 第四层池化:最大池化
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
# 进行扁平化
model.add(Flatten())
# 全连接层一:输出节点为120个
model.add(Dense(120, activation='relu'))
# 全连接层二:输出节点为84个
model.add(Dense(84, activation='relu'))
# 输出层:用softmax激活函数计算分类的概率
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) # 最后是10个数字,10个分类
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(), loss=keras.metrics.categorical_crossentropy, metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, batch_size=32, epochs=2, verbose=1)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels,verbose=0)
#model.save("A:\\code\\tensorflow\\course\\1_fashion_mnist\\mymodel")
print('损失:', loss)
print('准确率:', accuracy)
3.训练结果保存成冻结模型(pb文件)(train.py),训练结果保存为冻结模型的源码如下:
注:无需安装tensorflow也可以运行
#以下是生成pb的代码。注意:用model.save生成的pb文件不能被opencv调用
# Convert Keras model to ConcreteFunction
full_model = tf.function(lambda x: model(x))
full_model = full_model.get_concrete_function(
tf.TensorSpec(model.inputs[0].shape, model.inputs[0].dtype))
# Get frozen ConcreteFunction
frozen_func = convert_variables_to_constants_v2(full_model)
frozen_func.graph.as_graph_def()
layers = [op.name for op in frozen_func.graph.get_operations()]
print("-" * 50)
print("Frozen model layers: ")
for layer in layers:
print(layer)
print("-" * 50)
print("Frozen model inputs: ")
print(frozen_func.inputs)
print("Frozen model outputs: ")
print(frozen_func.outputs)
# Save frozen graph from frozen ConcreteFunction to hard drive
tf.io.write_graph(graph_or_graph_def=frozen_func.graph,
logdir=datapath+r"\frozen_models",
name="frozen_graph.pb",
as_text=False)
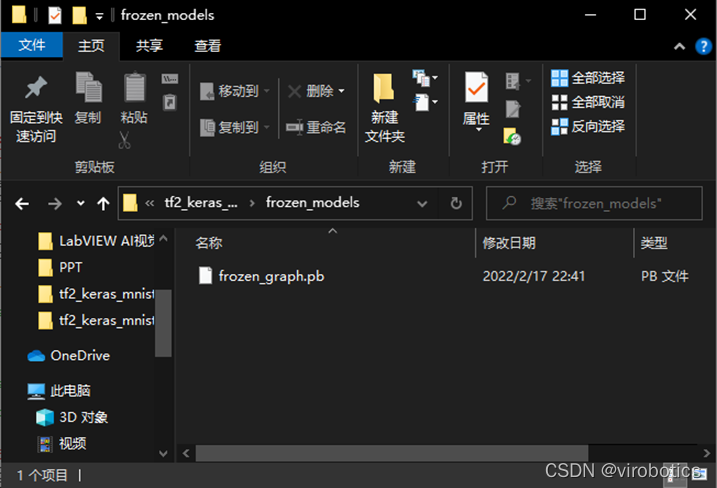
运行之后可生成如下图所示的pb模型:
4.python opencv调用冻结模型(cvcallpb.py)
import time
model_path = 'frozen_models\\frozen_graph.pb'
config_path = ''
#net = cv.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow(model_path, config_path)
import gzip
import os
import numpy as np
datapath=os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[0]
import cv2
def get_data():
train_image = datapath+r"\train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz"
test_image = datapath+r"\t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz"
train_label = datapath+r"\train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz"
test_label = datapath+r"\t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz"
paths = [train_label, train_image, test_label,test_image]
with gzip.open(paths[0], 'rb') as lbpath:
y_train = np.frombuffer(lbpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
with gzip.open(paths[1], 'rb') as imgpath:
x_train = np.frombuffer(
imgpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(len(y_train), 28, 28)
with gzip.open(paths[2], 'rb') as lbpath:
y_test = np.frombuffer(lbpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
with gzip.open(paths[3], 'rb') as imgpath:
x_test = np.frombuffer(
imgpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(len(y_test), 28, 28)
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels)=get_data()
def to_categorical(labels,number):
a=np.zeros((labels.shape[0],number),dtype=labels.dtype)
count=0
for i in labels:
a[count][i]=1
count+=1
return a
print(train_images.shape)
train_images = train_images.reshape(train_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1)
test_images = test_images.reshape(test_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1)
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels, 10)
test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels, 10)
# Load a model imported from Tensorflow
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow(model_path, config_path)
a=test_images[0].reshape(1,1,28,28)
net.setInput(a)
# Runs a forward pass to compute the net output
networkOutput = net.forward()
print(networkOutput)

三、LabVIEW OpenCV DNN实现手写数字识别
1、实现手写数字识别并实现MNIST数据简单的可视化(mnist_loadpb_simple.vi)
(1)读取mnist测试数据集二进制文件
 (2)载入pb神经网络模型
(2)载入pb神经网络模型
 (3)从二进制文件里读取某一幅图并显示出来
(3)从二进制文件里读取某一幅图并显示出来
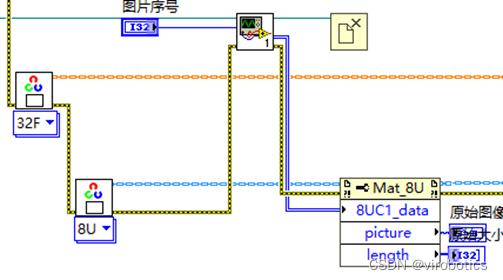 (4)blobImage,并把blob的结果用强度图显示出来
(4)blobImage,并把blob的结果用强度图显示出来
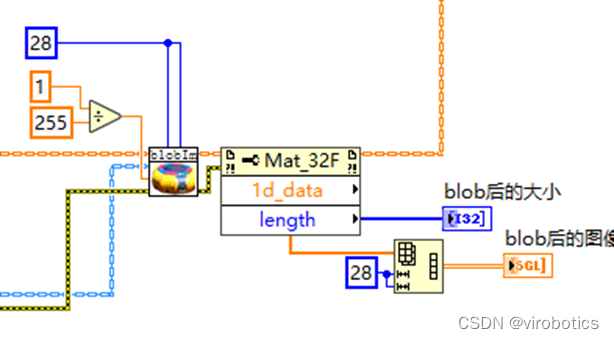 (5)把blob的结果送入神经网络推理,获取结果
(5)把blob的结果送入神经网络推理,获取结果
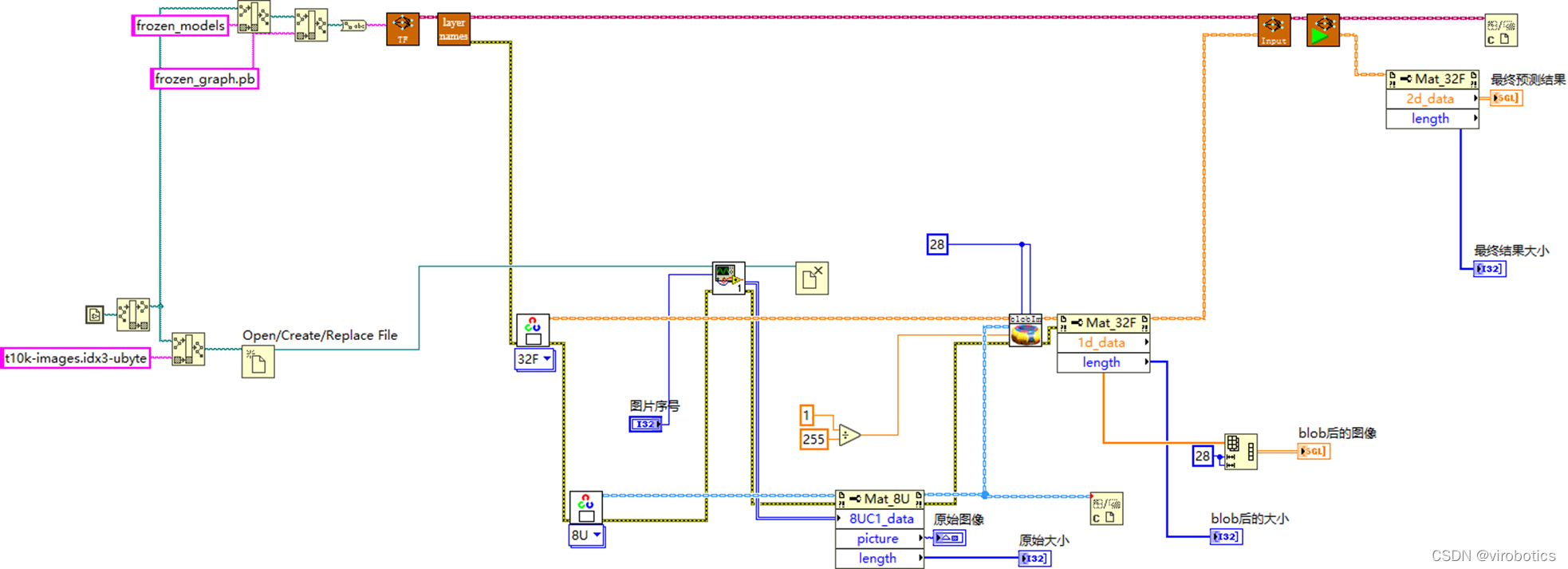
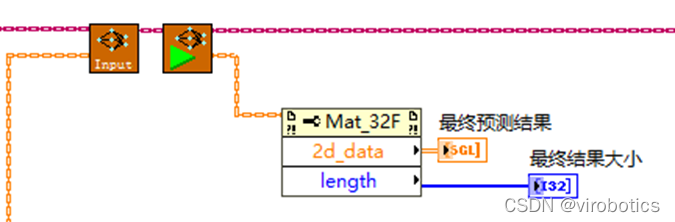 (6)总体源码及效果如下:
(6)总体源码及效果如下:
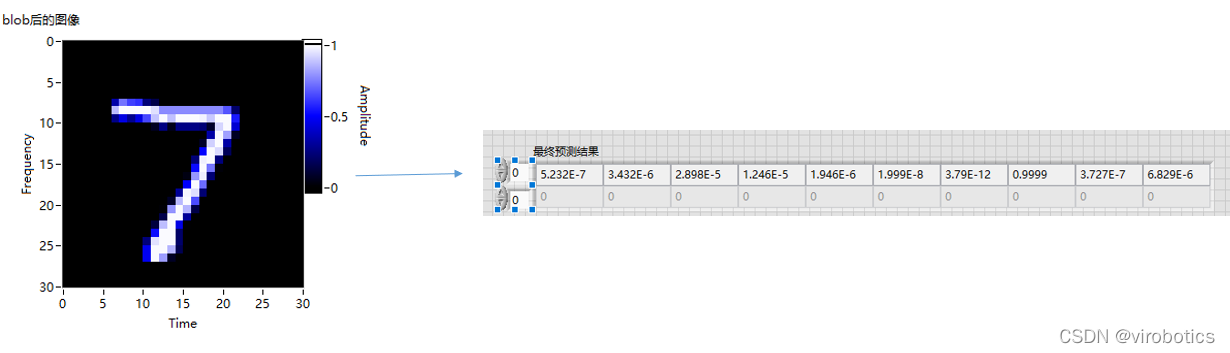
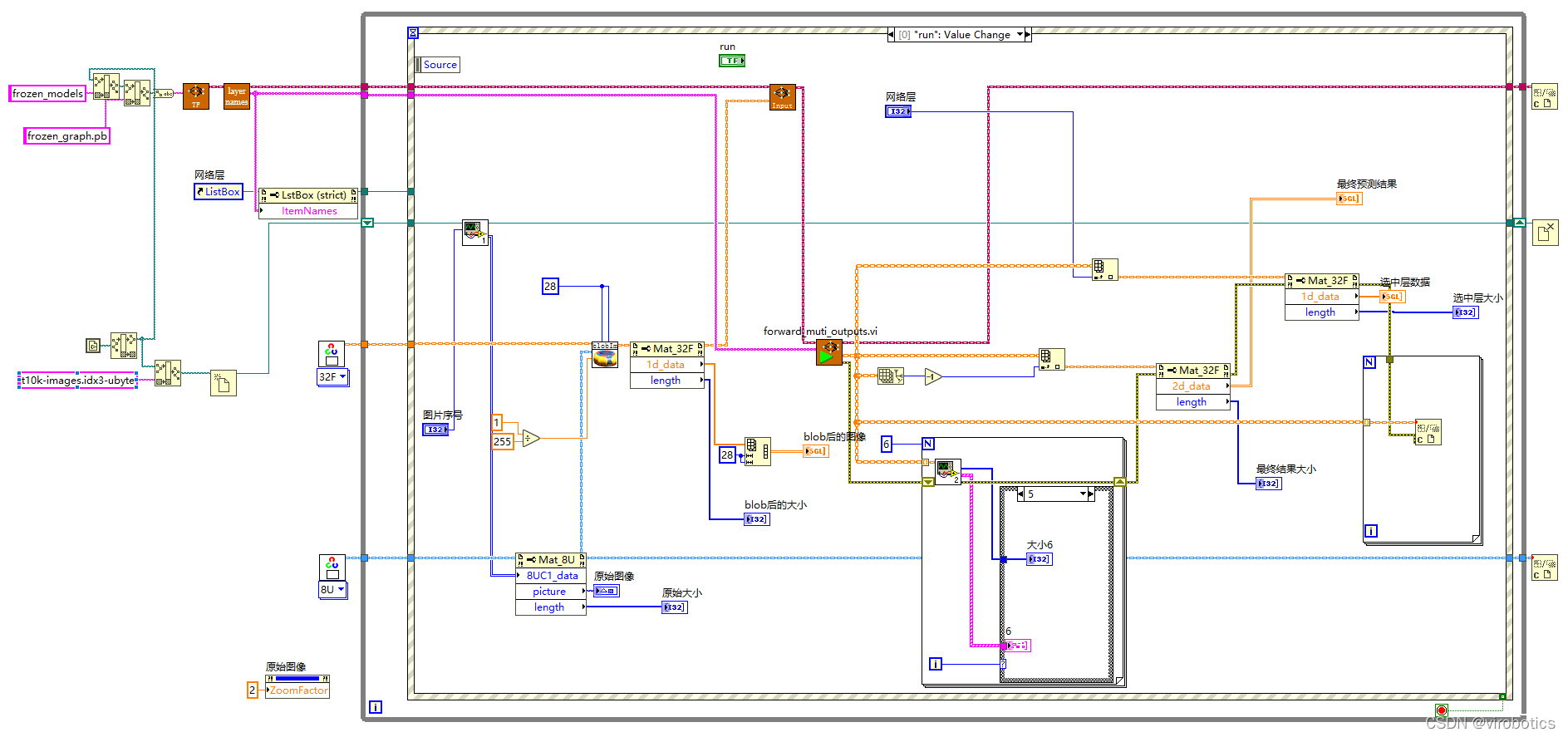
2、实现手写数字识别并实现MNIST数据高级的可视化(mnist_loadpb.vi)
与简单的可视化区别仅仅有以下几项:
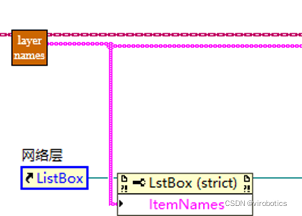
(1)多了getLayerName读出所有的网络层名字
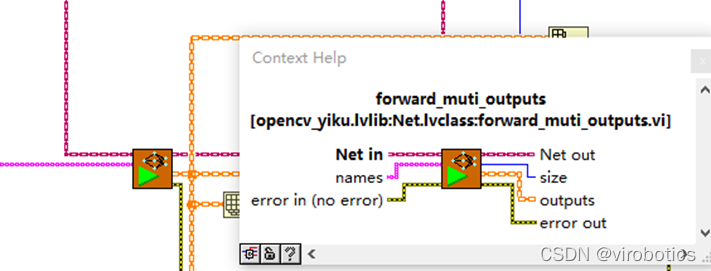
 (2)使用了多通道的forward(输入为名称数组)
(2)使用了多通道的forward(输入为名称数组)
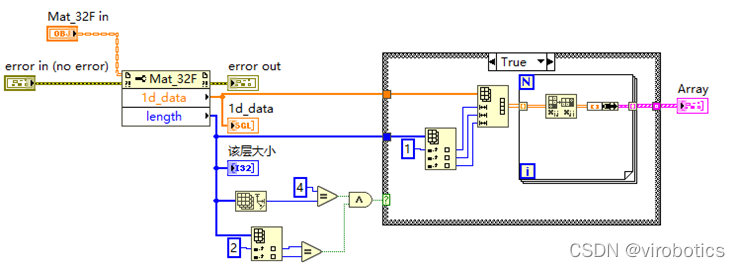
 (3)将前六层(两次卷积——relu——池化用强度图显示出来)
(3)将前六层(两次卷积——relu——池化用强度图显示出来)
 总体源码如下:
总体源码如下:
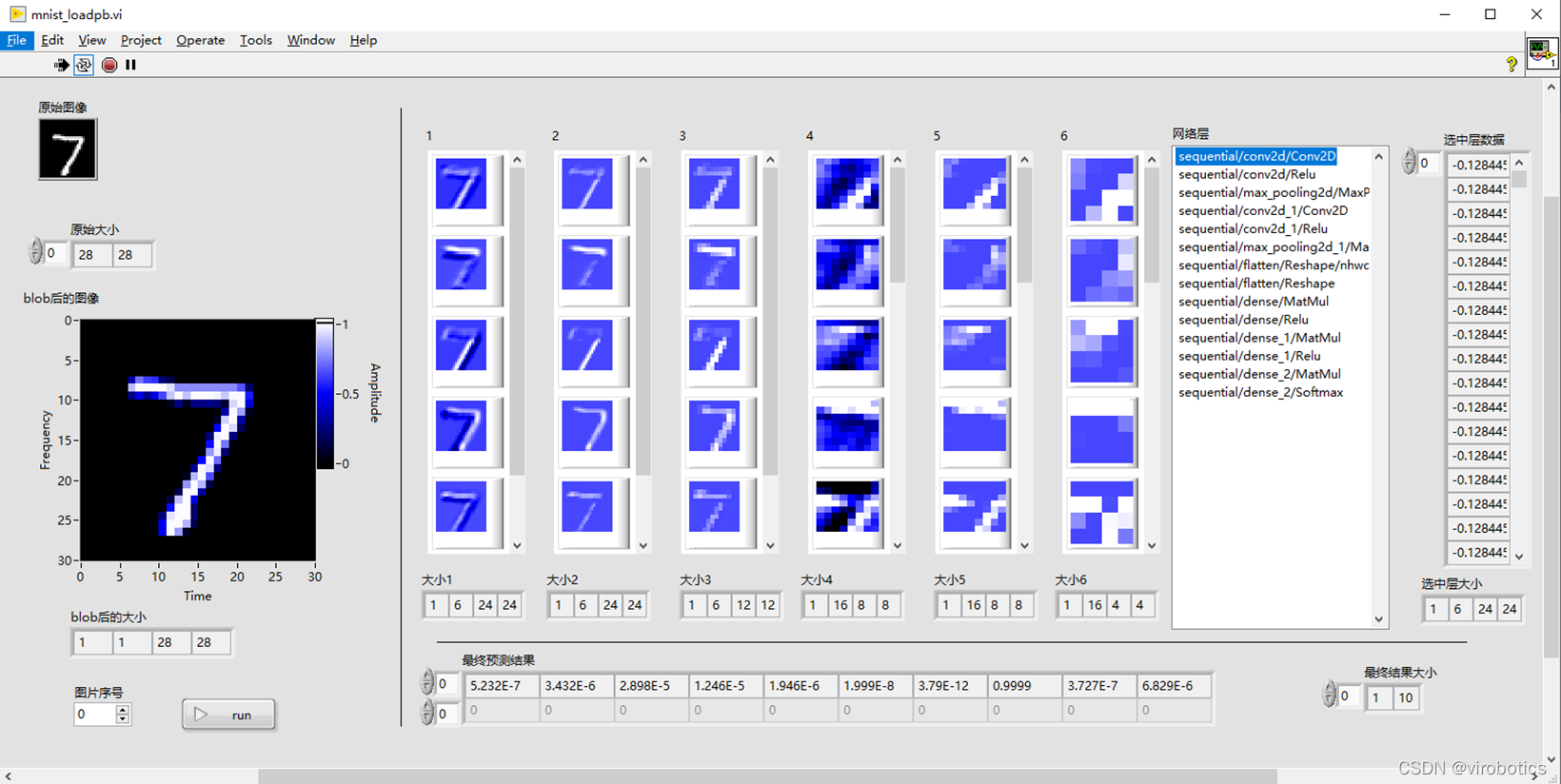
 运行效果如下:
运行效果如下:
四、源码下载
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NU_OcHgS0-5zNXQVkEt5uw 提取码:8888
总结
Q:我该使用tensorflow 1还是tensorflow 2? A:目前看tensorflow 1与opencv dnn模块、树莓派等开源硬件兼容性更好,且视觉对象检测的模型暂时更丰富。Tesnroflow 2的Keras函数训练神经网络非常方便,但对第三方软硬件兼容性还未做到最佳。估计随着后续版本的推出,TF2会逐渐成为主流。有些新的神经网络算子,慢慢地就不支持TF1了。同时opencv、开源硬件也会不断更新适应最新版本的TF。 另外,训练图像神经网络不用局限于TF,pytorch也是很好的选择。目前我们公司已逐渐从TF转向pytorch了。
Q:LabVIEW的opencv及其dnn模块支持哪些硬件和神经网络模型? A:提供多种框架模型导入模块:包括tensorflow、pytorch、darknet、openvino等多个平台的深度学习模型,官方的物体分类、物体检测、语义分割、实例分割都支持(后续会讲到),第三方的人脸识别、文字识别也已经通过验证。少量的高精度实例分割模型暂时不支持,后续我们会给大家介绍ONNX工具包,支持市面上几乎所有的模型。 支持的硬件方面,支持Nvidia GPU、Intel、TPU、NPU多种硬件加速。
更多关于LabVIEW与人工智能技术,可添加技术交流群进一步探讨。qq群号:705637299,请备注暗号:LabVIEW 机器学习
标签:

留言评论