JDBC和连接池02
3.ResultSet[结果集]
- 基本介绍
- 表示数据库结果集的数据表,通常通过执行查询数据库的语句生成
- ResultSet对象保持一个光标指向其当前的数据行,最初,光标位于第一行的之前
- next方法将光标移动到下一行,并且由于在ResultSet对象中没有更多行时返回false,因此可以在while循环中使用循环来遍历结果集
例子
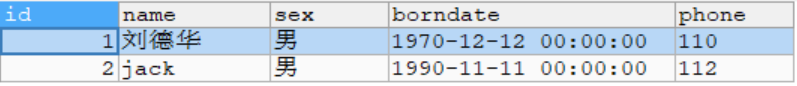
首先在数据库的actor表中添加两行数据
INSERT INTO actor VALUES(NULL,'刘德华','男','1970-12-12','110'),
(NULL,'jack','男','1990-11-11','112')
package li.jdbc.resultset_;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class ResultSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//通过Properties对象拿到配置文件的信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
//获取相关的值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);//建议写上
//2.得到连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//3.得到statement
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//4.组织sql
String sql = "select id,name,sex,borndate from actor";
//执行给定的sql语句,该语句返回单个ResultSet对象
/**
+----+-----------+-----+----------------------+
| id | name | sex | borndate |
+----+-----------+-----+----------------------+
| 1 | 刘德华 | 男 | 1970-12-12 00:00:00 |
| 2 | jack | 男 | 1990-11-11 00:00:00 |
+----+-----------+-----+----------------------+
*/
/**
* resultset源码 ResultSet对象的结构
*
*/
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//5.使用while循环取出数据
//最开始时next指向表头(第一行之前)
while (resultSet.next()) {//让光标向后移动,如果没有更多行,则返回false
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);//获取该行的第1列数据
String name = resultSet.getString(2);//获取该行的第2列数据
String sex = resultSet.getString(3);//获取该行的第3列数据
Date date = resultSet.getDate(4);//获取该行的第4列数据
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+date);
}
//6.关闭连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
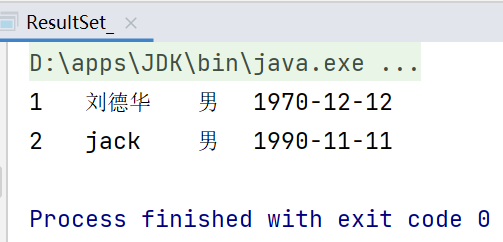
运行结果如下:
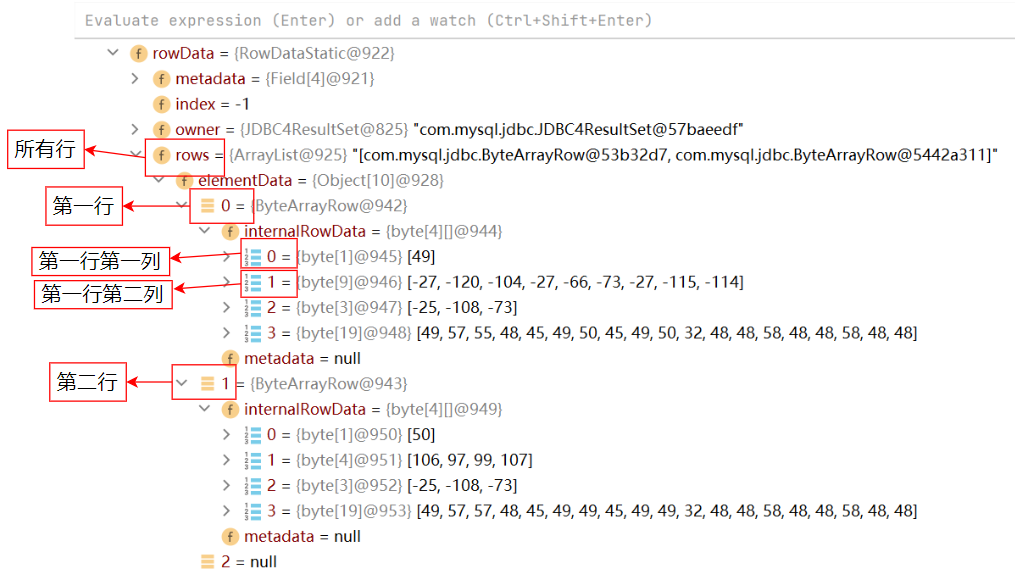
在语句ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);旁打上断点,点击debug,点击step over,选择resultset数组,再选择rowdata。

可以看到底层是arraylist的一个对象数组。
4.Statement
- 基本介绍
- Statement对象,用于执行静态SQL语句并返回其生成的结果的对象
- 在建立连接后,需要对数据库进行访问,执行命名或是SQL语句,可以通过
- Statement [存在SQL注入问题]
- PreparedStatement [预处理]
- CallableStatement [存储过程]
- Statement对象执行SQL语句,存在SQL注入风险
- SQL注入是利用某些系统没有对用户输入的数据进行充分的检查,而在用户输入数据中注入非法的SQL语句段或命令,恶意攻击数据库
- 要防范SQL注入,只要用PreparedStatement(从Statement扩展而来)取代Statement就可以了
例子1-sqlyog演示sql注入
-- 演示sql注入
-- 创建一张表
CREATE TABLE admin( -- 管理员表
NAME VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
pwd VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT ''
)CHARACTER SET utf8;
-- 添加数据
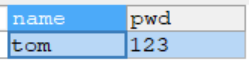
INSERT INTO admin VALUES('tom','123');
-- 正常情况下,查找某个管理是否存在
SELECT * FROM admin
WHERE NAME = 'tom' AND pwd = '123';
-- SQL注入
-- 输入用户名为 1' or
-- 输入密码为 or '1'='1
-- 这样就变成了下面的语句,可以将所有的数据都查找出来
SELECT * FROM admin
WHERE NAME = '1' OR' AND pwd = 'OR '1'='1';
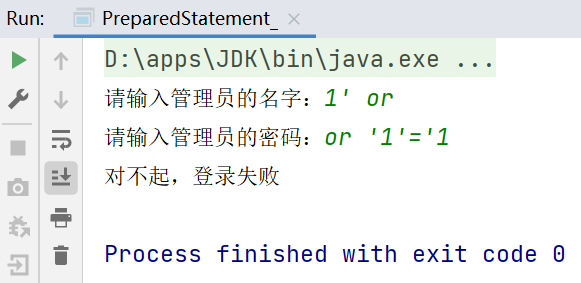
例子2-java程序演示SQL注入
package li.jdbc.statement;
//演示statement的注入问题
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Statement_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//让用户输入管理员的名字和密码
System.out.print("请输入管理员的名字:");
String admin_name = scanner.nextLine();//如果希望看到SQL注入,这里需要使用nextLine,如果用next():当接收到空格或者 '就是表示结束
System.out.print("请输入管理员的密码:");
String admin_pwd = scanner.nextLine();
//通过Properties对象拿到配置文件的信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
//获取相关的值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//2.获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//3.得到Statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//4.组织SQL语句
String sql = "select name,pwd from admin where name='"
+ admin_name + "' and pwd ='" + admin_pwd + "'";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()) {//如果查询到一条记录,则说明该管理员存在
System.out.println("恭喜,登录成功");
} else {
System.out.println("对不起,登录失败");
}
//5.关闭连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}

5.PreparedStatement[预处理查询]
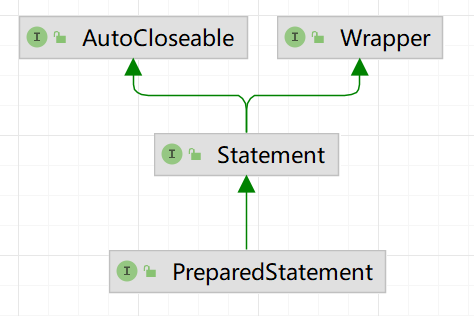
- 基本介绍
PreparedStatement执行的SQL语句中的 参数用问号(?)来表示,调用PreparedStatement对象的setXxx()方法来设置这些参数。
setXxx()方法有两个参数,第一个参数是要设置的SQL语句中的参数的索引(从1开始),第二个参数是设置的SQL语句中的参数的值
调用executeQuery(),返回ResultSet对象
调用executeUpdate():执行更新,包括增,删,修改
- 预处理的好处
- 不再使用+拼接sql语句,减少语法错误
- 有效地解决了SQL注入问题
- 大大减少了编译次数,效率较高
例子-解决SQL注入问题
package li.jdbc.preparedstatement_;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
//演示PreparedStatement的使用
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class PreparedStatement_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//让用户输入管理员的名字和密码
System.out.print("请输入管理员的名字:");
String admin_name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入管理员的密码:");
String admin_pwd = scanner.nextLine();
//通过Properties对象拿到配置文件的信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
//获取相关的值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//2.获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//3.得到PreparedStatement对象
//3.1组织SQL语句,sql语句的问号就相当于占位符
String sql = "select name,pwd from admin where name= ? and pwd = ?";
//3.2preparedStatement对象是实现了 PreparedStatement接口的 实现类的 对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.3给 ? 赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,admin_name);
preparedStatement.setString(2,admin_pwd);
//4.执行select语句使用 executeQuery
// 如果执行的是dml(update,insert,delete)语句使用executeUpdate
// 这里执行 executeQuery,不用再写sql进去了
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {//如果查询到一条记录,则说明该管理员存在
System.out.println("恭喜,登录成功");
} else {
System.out.println("对不起,登录失败");
}
//5.关闭连接
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
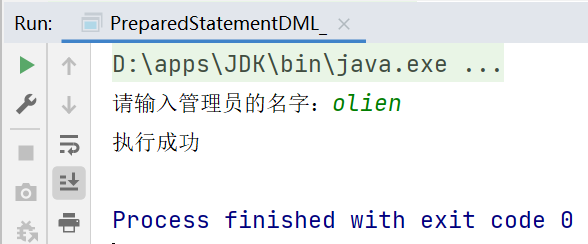
5.1预处理DML
package li.jdbc.preparedstatement_;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
//演示PreparedStatement的使用
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class PreparedStatementDML_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//让用户输入管理员的名字和密码
System.out.print("请输入管理员的名字:");
String admin_name = scanner.nextLine();
// System.out.print("请输入管理员的密码:");
// String admin_pwd = scanner.nextLine();
//通过Properties对象拿到配置文件的信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
//获取相关的值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//2.获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//3.得到PreparedStatement对象
//3.1组织SQL语句,sql语句的问号就相当于占位符
//添加记录
//String sql = "insert into admin values (?,?)";
//更改
//String sql = "update admin set pwd=? where name =?";
//删除
String sql = "delete from admin where name=?";
//3.2preparedStatement对象是实现了 PreparedStatement接口的 实现类的 对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.3给 ? 赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1, admin_name);
// preparedStatement.setString(2, admin_pwd);
//4.执行dml(update,insert,delete)语句使用executeUpdate
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");
//5.关闭连接
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
- 练习
参考上面的代码
- 创建admin表
- 使用PreparedStatement添加5条数据
- 修改tom的记录,将name改成King
- 删除一条记录
- 查询全部记录,并显示在控制台
6.JDBC API
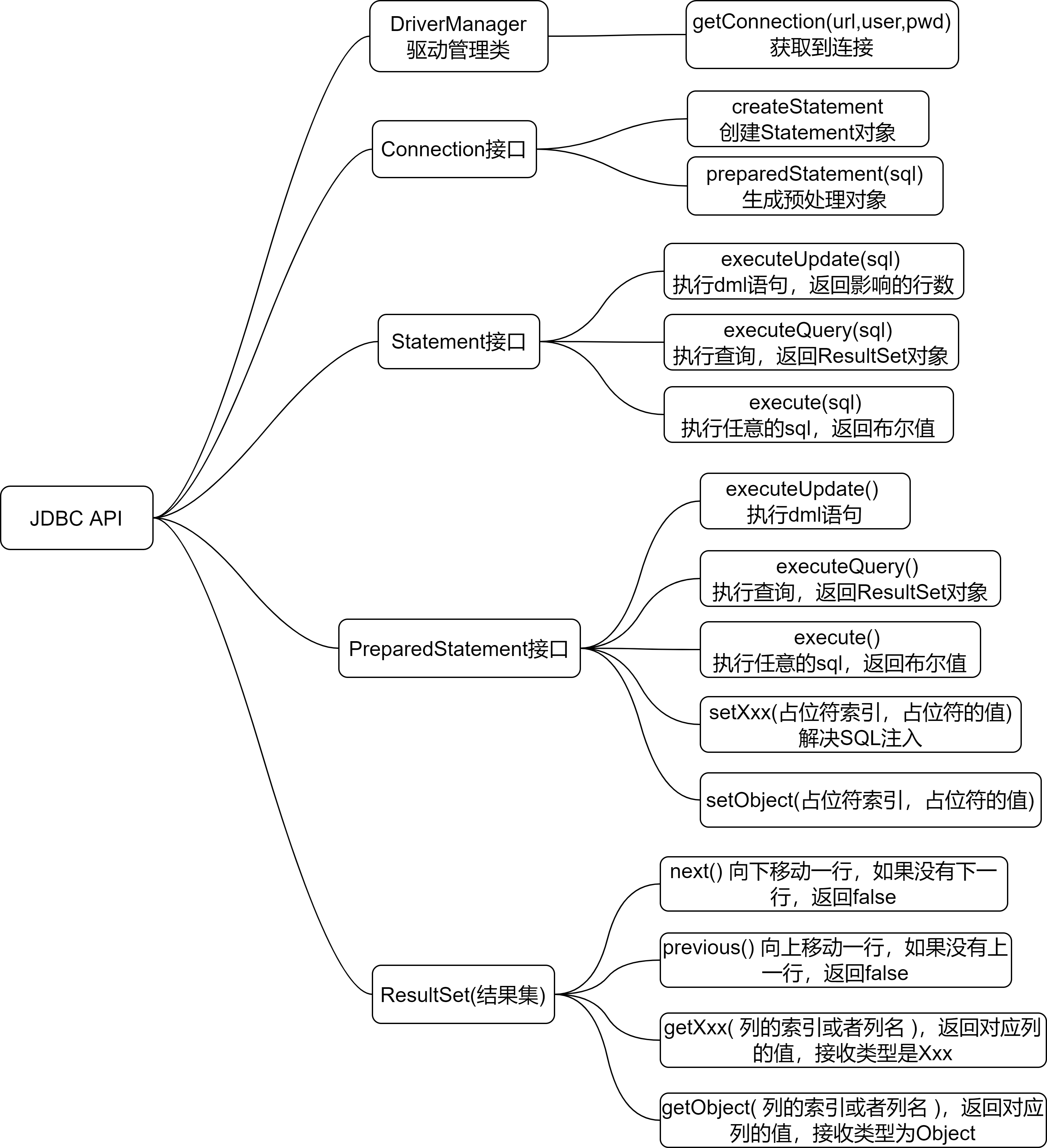
7.JDBCUtils开发
7.1封装JDBCUtils
- 说明
在jdbc操作中,获取连接和释放资源是经常使用到的,可以将其封装为JDBC连接的工具类JDBCUtils
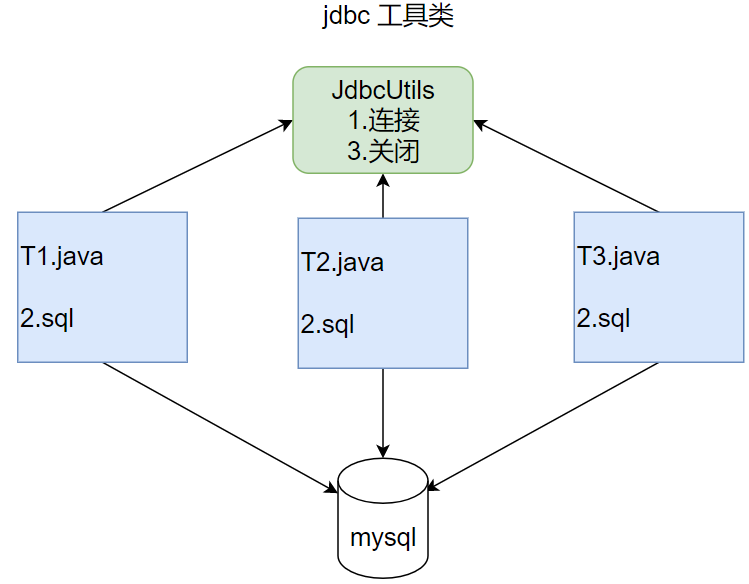
例子
封装的工具类JDBCUtils:
package li.jdbc.utils;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 这是一个工具类,完成mysql的连接和关闭资源
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
//定义相关的属性(4个),因为只需要一份,因此我们将其做成static属性
private static String user;//用户名
private static String password;//密码
private static String url;//url
private static String driver;//驱动名
//在static代码块去初始化
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
} catch (IOException e) {
//在实际开发中往往会这样处理
// 1.将 编译异常 转为 运行异常
// 2.这时调用者可以选择捕获该异常,亦可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便
// (对于运行异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throw的方式处理)
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//连接数据库,返回Connection
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
//将 编译异常 转为 运行异常,原因同上
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//关闭相关资源
/**
* 1.ResultSet 结果集
* 2.Statement 或者 PreparedStatement
* 3.Connection
* 4.如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则就传入null
*/
//这里用Statement作为参数接收,是因为Statement是PreparedStatement的父接口,
// 因此Statement参数既可以接收Statement的对象实现,也可以接收PreparedStatement类型的对象实现
public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection) {
//判断是否为null
try {
if (set != null) {
set.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
//将 编译异常 转为 运行异常,原因同上
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
使用测试JDBCUtils_Use:
package li.jdbc.utils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 该类演示如何使用JDBCUtils工具类,完成 dml和 select
*/
public class JDBCUtils_Use {
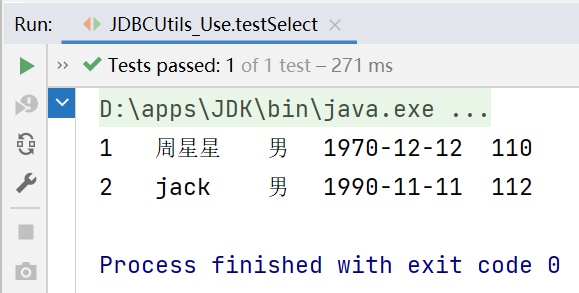
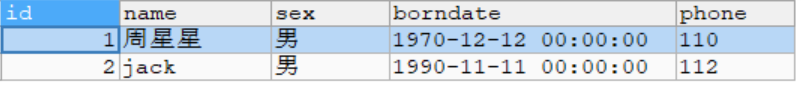
@Test
public void testSelect() {//insert update delete
//1.得到连接
Connection connection = null;
//2.组织一个sql语句
String sql = "Select * from actor";
//3.创建PreparedStatement对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet set = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//执行sql,得到结果集
set = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//遍历该结果集
while (set.next()) {
int id = set.getInt("id");
String name = set.getString("name");
String sex = set.getString("sex");
Date borndate = set.getDate("borndate");
String phone = set.getString("phone");
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + sex + "\t" + borndate + "\t" + phone);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtils.close(set, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
@Test
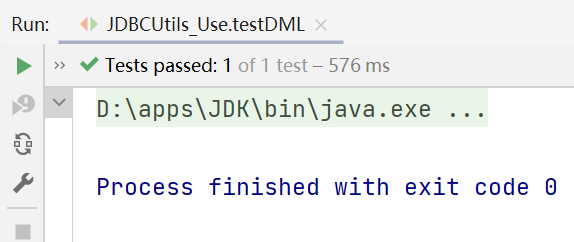
public void testDML() {//insert update delete
//1.得到连接
Connection connection = null;
//2.组织一个sql语句
String sql = "update actor set name=? where id=?";
//3.创建PreparedStatement对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1, "周星星");//第1个占位符的值为周星星
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 1);//第2个占位符的值为1
//执行sql
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
运行结果:
标签:

留言评论